 Commissioning for Compliance with Industry Standards: A Focus on Tier Classification
Commissioning for Compliance with Industry Standards: A Focus on Tier Classification
What's the most important thing for a data center? That is the uptime!
Among the most widely recognized standards in the data center industry is the Tier Classification system developed by the Uptime Institute. This system is a framework for assessing and certifying the design and operational capabilities of data center facilities based on their resilience and redundancy levels.
Looking for more information on the different levels you need to test? Then visit our article on Data center level testing.
Understanding the Tier Classification System:
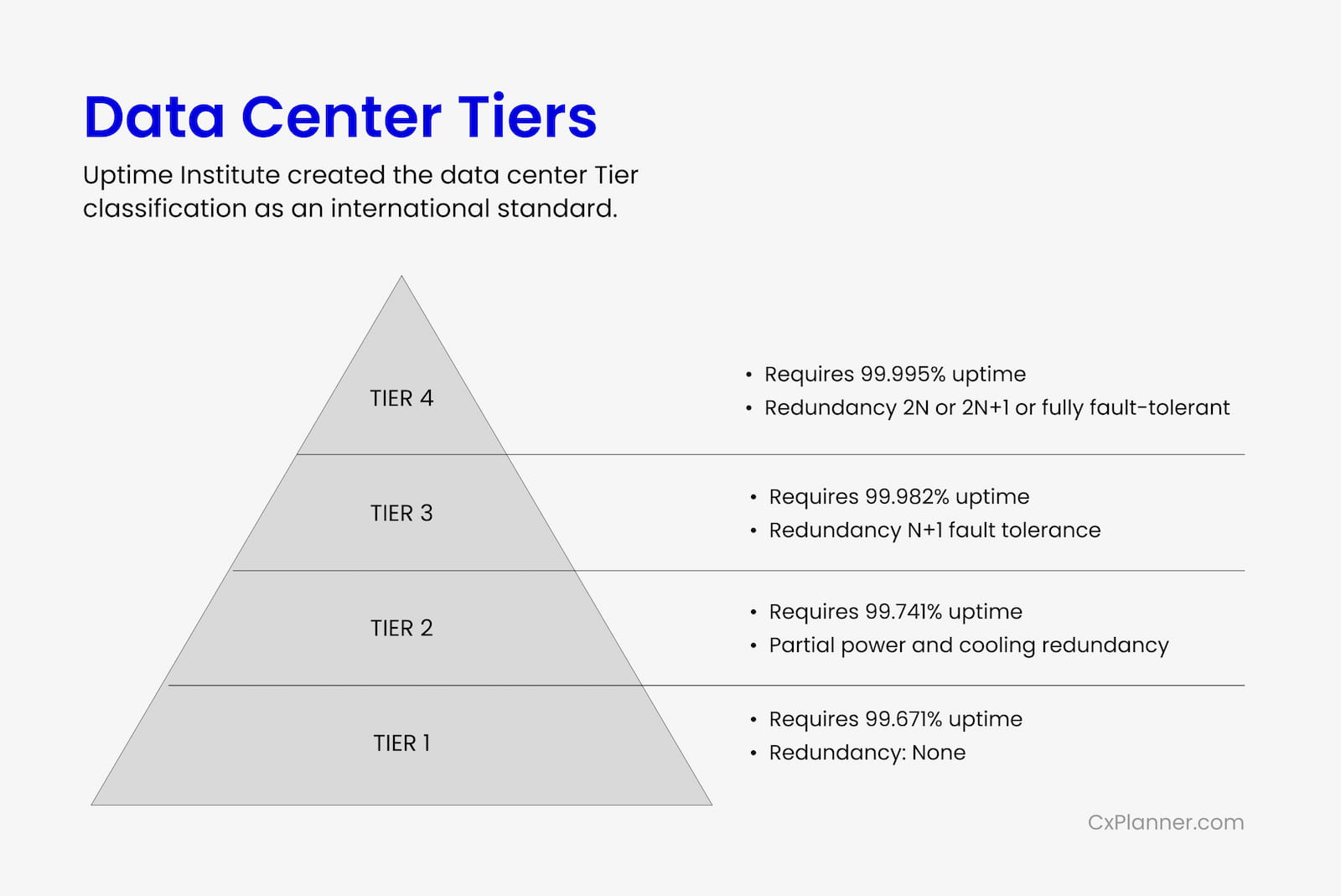
The Tier Classification system categorizes data centers into four tiers, ranging from Tier I to Tier IV, based on their infrastructure design, availability, and fault tolerance.
Each tier represents a progressively higher level of resilience and redundancy, with Tier IV being the most robust and fault-tolerant.
Commissioning Requirements for Each Tier:
Commissioning plays a role in achieving and maintaining compliance with Tier standards. Depending on the desired Tier level, data center commissioning processes must align with specific requirements to ensure that infrastructure components and systems meet the necessary performance criteria.
Tier I:
Data centers at Tier I level typically have basic infrastructure components and limited redundancy. Commissioning activities focus on verifying basic functionality and ensuring compliance with minimum uptime requirements.
Tier II:
At Tier II, data centers incorporate some redundancy in critical systems to enhance reliability. Commissioning efforts include testing redundant components, assessing fault tolerance, and validating failover mechanisms to minimize downtime risks.
Tier III:
Tier III data centers feature concurrently maintainable infrastructure, allowing for maintenance and upgrades without disrupting operations. Commissioning procedures emphasize the validation of redundant paths, fault tolerance levels, and concurrent maintainability to achieve high availability and uptime.
Tier IV:
Data centers at Tier IV level are designed to withstand the most severe disruptions with fault-tolerant architecture and multiple independent systems. Commissioning activities focus on rigorous testing of redundant components, fault isolation mechanisms, and fault tolerance capabilities to ensure continuous operation under any circumstance.
 Uptime Institute Tier Classification System
Uptime Institute Tier Classification System
The Uptime Institute's Tier Classification system is a globally recognized standard for evaluating and certifying the design, construction, and operation of data center infrastructure. Developed by the Uptime Institute, a leading authority on data center reliability and performance, the Tier Classification system provides a framework for assessing the resilience, redundancy, and availability of data center facilities.
Commissioning for compliance with industry standards, particularly the Tier Classification system, is essential for ensuring the reliability, resilience, and performance of data center facilities.
By aligning commissioning processes with Tier requirements and undergoing rigorous testing and validation, data center operators can achieve certification and demonstrate their commitment to delivering mission-critical services with utmost reliability and availability.
 Practical examples of testing
Practical examples of testing
Tier I: Basic Capacity and Redundancy
- Power Capacity Testing: Conduct load testing on power distribution systems to verify capacity and identify any limitations or bottlenecks.
- Cooling Capacity Testing: Assess the cooling capacity of HVAC systems under full load conditions to ensure adequate temperature control and prevent overheating.
- Redundancy Verification: Test backup power sources, such as generators and UPS systems, to validate their functionality and ability to maintain operations during power outages.
Tier II: Redundant Capacity Components
- Redundant Path Testing: Validate redundant power and cooling paths to ensure seamless failover in the event of component failure or maintenance activities.
- Concurrent Maintainability Testing: Perform simulated maintenance procedures on critical infrastructure components to assess the facility's ability to maintain operations without downtime.
- Fault Tolerance Testing: Test failover mechanisms and automatic transfer switches to verify their ability to quickly switch between primary and backup systems without interruption.
Tier III: Concurrently Maintainable
- Concurrent Maintenance Simulation: Conduct live testing of maintenance procedures on redundant components while the facility remains operational, ensuring continuous uptime during maintenance activities.
- Fault Isolation Testing: Simulate component failures and assess the facility's ability to isolate faults without impacting overall operations, demonstrating fault tolerance and resiliency.
- Redundant Component Load Balancing: Verify load balancing across redundant components to ensure optimal utilization and prevent overloading in case of component failure.
Tier IV: Fault Tolerant
- Full Load Redundancy Testing: Test redundant components under full load conditions to validate their ability to handle peak demand without compromising performance or reliability.
- Simulated Disaster Scenarios: Conduct simulated disaster scenarios, such as power grid failures or equipment malfunctions, to evaluate the facility's response and resilience to extreme conditions.
- Zero Downtime Maintenance: Demonstrate the ability to perform maintenance on critical systems without any impact on operations, utilizing redundant paths and fault-tolerant architecture.
By tailoring commissioning activities and tests to the specific requirements of each tier, data center operators can validate the resilience, redundancy, and fault tolerance of their facilities, ensuring compliance with industry standards and delivering high levels of reliability and availability.
 Managing the commissioning process with CxPlanner
Managing the commissioning process with CxPlanner
CxPlanner has been built to facilitate the commissioning process on data centers. As a dedicated commissioning software solution tailored specifically for data centers, you will find easy and structured workflows for all the levels, documentation generation, and compliance with industry standards, including the Uptime Institute's Tier Classification system.
Key Features of CxPlanner:
- Centralized Management: CxPlanner provides a centralized platform for managing all aspects of commissioning verification, from planning and scheduling to execution and documentation. It offers a single source of truth for stakeholders to track progress, collaborate on tasks, and access critical information related to commissioning activities.
- Structured Templates and Requirements: CxPlanner comes equipped with predefined templates and requirements tailored to each tier of the Uptime Institute's Tier Classification system. These templates outline the specific tests, procedures, and documentation requirements necessary to achieve compliance with Tier standards, ensuring consistency and adherence to best practices.
- Level-Based Testing Management: CxPlanner facilitates the management of commissioning verification activities across different levels of testing, from Level 1 to Level 5. It allows users to define test plans, assign tasks, and track completion status for each level, ensuring a systematic and comprehensive approach to verification.
- Automated Documentation Handover: One of the standout features of CxPlanner is its ability to automate the documentation handover process. Upon completion of commissioning activities, the software generates comprehensive documentation packages, including test reports, compliance certificates, and equipment records, ready for submission to stakeholders and regulatory authorities.
- Real-Time Reporting and Analytics: CxPlanner provides real-time reporting and analytics capabilities, allowing stakeholders to monitor key performance indicators, track project milestones, and identify areas for improvement. It offers insights into commissioning progress, compliance status, and potential risks, enabling informed decision-making and proactive intervention.
Try CxPlanner on your next data center project